PS/Algorithms
[Java] Fenwick Tree(Binary Indexed Tree, BIT) - O(lgN)의 부분합 계산
CalicoCat22
2022. 1. 19. 20:12
https://www.acmicpc.net/blog/view/21
펜윅 트리 (바이너리 인덱스 트리)
블로그: 세그먼트 트리 (Segment Tree) 에서 풀어본 문제를 Fenwick Tree를 이용해서 풀어보겠습니다. Fenwick Tree는 Binary Indexed Tree라고도 하며, 줄여서 BIT라고 합니다. Fenwick Tree를 구현하려면, 어떤 수 X
www.acmicpc.net
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2042
2042번: 구간 합 구하기
첫째 줄에 수의 개수 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000,000)과 M(1 ≤ M ≤ 10,000), K(1 ≤ K ≤ 10,000) 가 주어진다. M은 수의 변경이 일어나는 횟수이고, K는 구간의 합을 구하는 횟수이다. 그리고 둘째 줄부터 N+1번째 줄
www.acmicpc.net
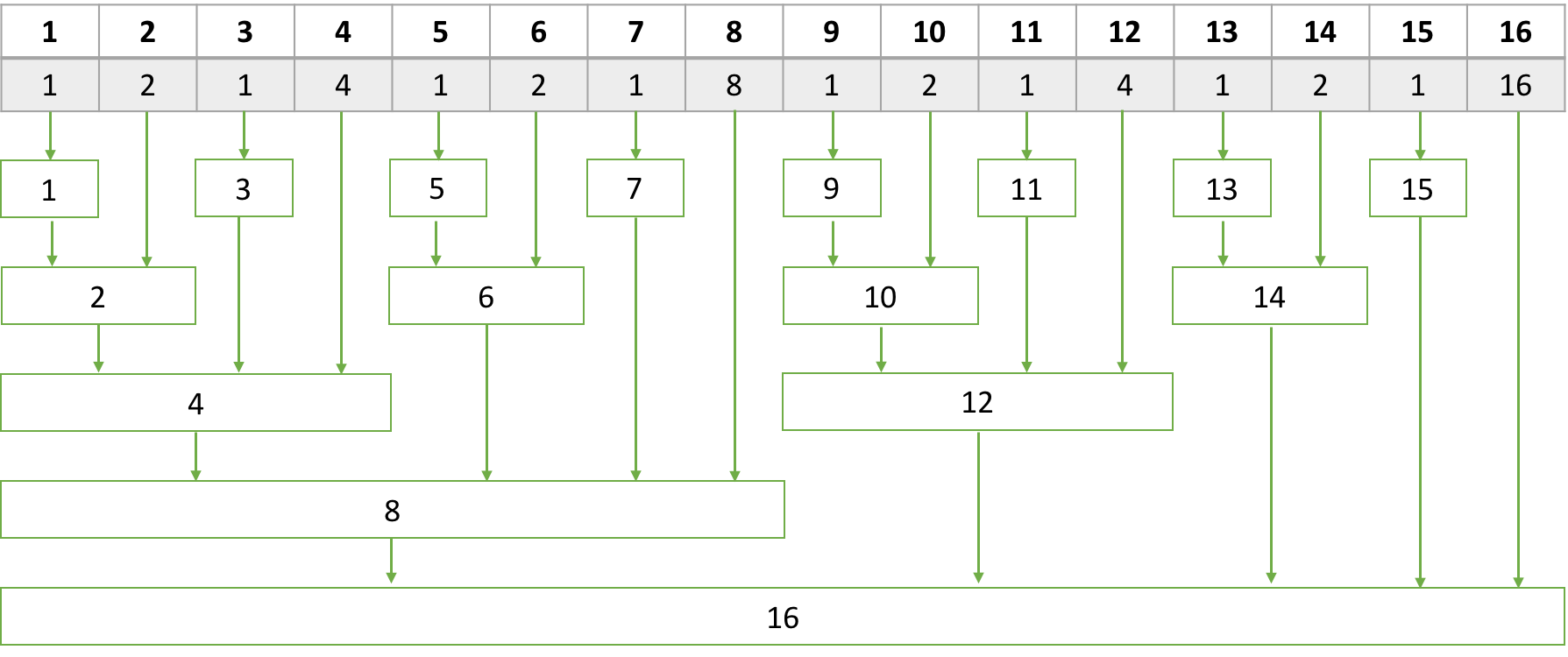
update는 index가 포함된 모든 tree에 대하여 => i += (i & -i)
sum은 i -= (i & -i) 에 대하여
* (i & -i) 는 i를 이진수로 나타냈을 때 가장 우측에 나오는 1이 나타내는 수를 의미
=> tree[i]는 (i & -i) 개의 칸에 대한 정보를 담고 있다.
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class g1_2042{
static FastScanner fs = new FastScanner();
static PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(System.out);
static int n, m, k;
static long[] tree, pp;
public static void main(String[] args){
n = fs.nextInt();
m = fs.nextInt();
k = fs.nextInt();
pp = new long[n + 1];
// 해당 칸의 원래 값
tree = new long[n + 1];
// 해당 index까지 (i&-i)개의 칸의 합
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){
pp[i] = fs.nextLong();
update(i, pp[i]);
}
for (int t=0;t<m+k;t++){
if (fs.nextInt() == 1){
int index = fs.nextInt();
long num = fs.nextLong();
update(index, num - pp[index]);
pp[index] = num;
}
else{
int left = fs.nextInt();
int right = fs.nextInt();
pw.println(sum(right) - sum(left - 1));
}
}
pw.close();
}
static void update(int i, long num){
while (i <= n){
tree[i] += num;
i += (i & -i);
}
}
static long sum(int i){
long ans = 0;
while (i > 0){
ans += tree[i];
i -= (i & -i);
}
return ans;
}
// ----------input function----------
static void sort(int[] a){
ArrayList<Integer> L = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i : a) L.add(i);
Collections.sort(L);
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) a[i] = L.get(i);
}
static class FastScanner{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer("");
String next(){
while (!st.hasMoreTokens()){
try{
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt(){
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
int[] readArray(int n){
int[] a = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) a[i] = nextInt();
return a;
}
long nextLong(){
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
}
}